Other Name(s):
Acide Alpha-Linolénique, Ácido Alfa Linolénico, Acide Gras Essentiel, ALA, Acide Linolénique, Acide Gras N3, Acide Gras Oméga 3, Acide Gras Polyinsaturé Oméga 3, Acide Gras Polyinsaturé N3, Essential Fatty Acid, Linolenic Acid, LNA, N-3 Fatty Acid, N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid, Omega 3, Omega 3 Fatty Acids, Omega-3, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid.
CAS No. | 463-40-1 |
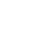
| Structure |  |
| Synonyms | alpha-Linolenic acid; linolenic acid; linolenate; Octadeca-9Z,12Z,15Z-Trienoic acid; (Z,Z,Z)-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid; 9,12,15-Octadecatrienic acid; 9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid; 9Z,12Z,15Z-Octadecatrienoic acid; alpha-LNN; all cis-9,12,15-Octadecatrienoic acid |
| IUPAC Name | (9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 278.43 |
| Molecular Formula | C18H30O2 |
| Canonical SMILES | CCC=CCC=CCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)O |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H30O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18(19)20/h3-4,6-7,9-10H,2,5,8,11-17H2,1H3,(H,19,20)/b4-3-,7-6-,10-9- |
| InChIKey | DTOSIQBPPRVQHS-PDBXOOCHSA-N |
| Melting Point | -11°C |
| Flash Point | 275.7°C |
| Purity | >98% |
| Density | 0.914 g/cm3 |
| Solubility | water, 0.1236 mg/L @ 25 °C (est) |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow liquid |
| Application | Ingredient of health care products. |
| Storage | 2-8°C |
| EINECS | 207-334-8 |
| MDL | MFCD00065720 |
| Quality Standard | Enterprise Standard |
| Refractive Index | 1.48 |
| Stability | Stable under normal temperatures and pressures. |
| Description | α-Linolenic acid (ALA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that occurs as the glyceride in most drying oils. It has an inhibitory effect on prostaglandin thus reduces inflammation and the risk of certain chronic diseases. Nutritional supplement in health care products. |
OVERVIEW
Alpha-linolenic acid is an essential omega-3 fatty acid. It is called "essential" because it is needed for normal human growth and development. Nuts, such as walnuts, are good sources of alpha-linolenic acid. It is also found in vegetable oils such as flaxseed (linseed) oil, canola (rapeseed) oil, and soybean oil, as well as in red meat and dairy products.
Alpha-linolenic acid is popular for preventing and treating diseases of the heart and blood vessels. It is used to prevent heart attacks, lower high blood pressure, lower cholesterol, and reverse "hardening of the blood vessels" (atherosclerosis). There is some evidence that alpha-linolenic acid from dietary sources might be effective for all these uses except lowering cholesterol. Not enough is known yet to be able to rate alpha-linolenic acid's effect on high cholesterol.
Alpha-linolenic acid is used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA), multiple sclerosis (MS), lupus, diabetes, renal disease, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn's disease. It is also used to prevent pneumonia.
Other uses include treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), migraine headache, skin cancer, depression, and allergic and inflammatory conditions such as psoriasis and eczema.
Some people use alpha-linolenic acid to prevent cancer. Ironically, alpha-linolenic acid may actually raise some men's risk of getting prostate cancer.
You have probably heard a lot about other omega-3 fatty acids such as EPA and DHA, which are found in fish oil. Be careful. Not all omega-3 fatty acids act the same way in the body. Alpha-linolenic acid may not have the same benefits as EPA and DHA.
How does work?
Alpha-linolenic acid is thought to decrease the risk of heart disease by helping to maintain normal heart rhythm and heart pumping. It might also reduce blood clots. Although alpha-linolenic acid seems to benefit the cardiovascular system and might reduce the risk of heart disease, research to date does not show it has a significant effect on cholesterol levels.